
kashimotoxiang
4/19/2019 - 5:51 AM
python - algorithm
# traditional memory
mem = {}
def search(dim1, dim2):
# try to retrieve
if (dim1, dim2) in mem:
return mem[(dim1, dim2)]
# calculate the value ...
# store
mem[(dim1, dim2)] = value
return value
# is equivalent to
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=dpsize)
def search(dim1, dim2):
# automatically store the return value indexed by the parameters
# calculate the value ...
return value
ptr = root
while ptr:
if ptr.left:
probe = ptr.left
while probe.right and probe.right != ptr:
probe = probe.right
if probe.right == ptr: # return to ascendant
probe.right = None
ptr = ptr.right # to right
else:
probe.right = ptr
ptr = ptr.left # to left
else:
ptr = ptr.right
def search(s, p): # s: full text, p: pattern
if not p: return 0
if not s: return -1
nxt = [-1]
ptr = 0
for char in p[1:]:
nxt.append(nxt[ptr] if char == p[ptr] else ptr)
while ptr >= 0 and char != p[ptr]:
ptr = nxt[ptr]
ptr += 1
ptr = 0
for ind, char in enumerate(s):
while ptr >= 0 and char != p[ptr]:
ptr = nxt[ptr]
ptr += 1
if ptr == len(p):
return ind-len(p)+1
class RabinKarpHash:
def __init__(self, base, mod=int(1e9+7)):
self.base = base
self.mod = mod
def hash(self, arr):
h = 0
for val in arr:
h = ((h * self.base) + val) % self.mod
return h
def roll(self, origin_hash, drop_val, new_val, max_base):
h = origin_hash - (drop_val * max_base % self.mod)
h = ((h*self.base)+new_val+self.mod)%self.mod
return h
def get_max_base(self, length):
ret = 1
for i in range(length-1):
ret = (ret*self.base) % self.mod
return ret
小 trick
overlap条件:start1 < end2 and end1 > start2
在DFS中我们说关键点是递归以及回溯,在BFS中,关键点则是状态的选取和标记
树算法
Binary Indexed Tree BIT 树状数组
class BIT:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n + 1
self.sums = [0] * self.n
def update(self, i, delta):
while i < self.n:
self.sums[i] += delta
i += i & (-i) # = i & (~i + 1) 用于追踪最低位的1
def prefixSum(self, i):
res = 0
while i > 0:
res += self.sums[i]
i -= i & (-i)
return res
def rangeSum(self, s, e):
return self.prefixSum(e) - self.prefixSum(s - 1)
Binary Search Tree
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
def search(self, data, parent=None):
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
return None, None
return self.left.search(data, self)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
return None, None
return self.right.search(data, self)
else:
return self, parent
Trie
import collections
class TrieNode():
def __init__(self):
self.children = collections.defaultdict(TrieNode)
self.isEnd = False
class Trie():
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
node = self.root
for w in word:
node = node.children[w]
node.isEnd = True
def search(self, word):
node = self.root
for w in word:
# dict.get() 找不到的话返回None
node = node.children.get(w)
if not node:
return False
return node.isEnd
线段树
class SegmentTree(object):
def __init__(self, nums, s=None, e=None): # build
self.lo, self.hi = s, e
self.left, self.right = None, None
self.mid = (self.lo+self.hi)/2
self.val = 0
if self.hi < self.lo:
return
elif self.hi == self.lo:
self.val = nums[self.lo]
else: # self.lo < self.hi
self.left = SegmentTree(nums, self.lo, self.mid)
self.right = SegmentTree(nums, self.mid+1, self.hi)
self.val = self.left.val + self.right.val
def update(self, i, val): # modify
if i == self.lo == self.hi:
self.val = val
else:
if i <= self.mid:
self.left.update(i, val)
else:
self.right.update(i, val)
self.val = self.left.val + self.right.val
def sumRange(self, i, j): # query
if i == self.lo and j == self.hi: # equal
return self.val
elif self.lo > j or self.hi < i: # not intersect
return 0
else: # intersect
if i > self.mid: # all at the right sub tree
return self.right.sumRange(i, j)
elif j <= self.mid: # all at the left sub tree
return self.left.sumRange(i, j)
else: # some at the right & some at the left
return self.left.sumRange(i, self.mid) + self.right.sumRange(self.mid+1, j)
def get(self, i):
if self.lo == self.hi == i:
return self.val
elif self.lo > i or self.hi < i:
return 0
else:
if i > self.mid: # right
return self.right.get(i)
else: # left
return self.left.get(i)
排序算法
快速选择
quick select
def partition(nums, lo, hi):
i, x = lo, nums[hi]
for j in range(lo, hi):
if nums[j] <= x:
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
i += 1
nums[i], nums[hi] = nums[hi], nums[i]
return i
def quick_select(nums, lo, hi, k):
while lo < hi:
mid = partition(nums, lo, hi)
if mid == k:
return nums[k]
elif mid < k:
lo = mid+1
else:
hi = mid-1
nums = [54, 26, 93, 17, 77, 31, 44, 55, 20]
for i in range(len(nums)):
print(quick_select(nums, 0, len(nums)-1, i))
selection sort
def selection_sort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums), 0, -1):
tmp = 0
for j in range(i):
if not compare(nums[j], nums[tmp]):
tmp = j
nums[tmp], nums[i-1] = nums[i-1], nums[tmp]
return nums
quick sort, in-place
def quick_sort(nums, l, r):
if l >= r:
return
pos = partition(nums, l, r)
quick_sort(nums, l, pos-1)
quick_sort(nums, pos+1, r)
def partition(nums, lo, hi):
i, x = lo, nums[hi]
for j in range(lo, hi):
if nums[j] <= x:
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
i += 1
nums[i], nums[hi] = nums[hi], nums[i]
return i
arr = [4, 2, 1, 23, 2, 4, 2, 3]
quick_sort(arr, 0, len(arr)-1)
print(arr)
bubble sort
def bubble_sort(nums):
for i in reversed(range(len(nums))):
for j in range(i-1):
if not compare(nums[j], nums[j+1]):
nums[j], nums[j+1] = nums[j+1], nums[j]
return nums
insertion sort
def insertion_sort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums)):
pos, cur = i, nums[i]
while pos > 0 and not compare(nums[pos-1], cur):
nums[pos] = nums[pos-1] # move one-step forward
pos -= 1
nums[pos] = cur
return nums
merge sort
def merge_sort(nums):
nums = mergeSort(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
return str(int("".join(map(str, nums))))
def mergeSort(nums, l, r):
if l > r:
return
if l == r:
return [nums[l]]
mid = (r+l)//2
left = mergeSort(nums, l, mid)
right = mergeSort(nums, mid+1, r)
return merge(left, right)
def merge(l1, l2):
res, i, j = [], 0, 0
while i < len(l1) and j < len(l2):
if not compare(l1[i], l2[j]):
res.append(l2[j])
j += 1
else:
res.append(l1[i])
i += 1
res.extend(l1[i:] or l2[j:]) # 喵🐱
return res
图论算法
拓扑排序
两个defaultdict 一个graph,一个in_degree
from collections import defaultdict
def findOrder(numCourses, prerequisites):
graph = defaultdict(list)
in_degree = defaultdict(int)
for dest, src in prerequisites:
graph[src].append(dest)
in_degree[dest] += 1
zero_degree = [k for k, v in in_degree.items() if v == 0]
res = []
while zero_degree:
node = zero_degree.pop(0)
res.append(node)
for child in graph[node]:
in_degree[child] -= 1
if in_degree[child] == 0:
zero_degree.append(child) # 同时也说这个元素该删除了
return res
普利姆(Prime)算法
每个节点选cost最小的边
from collections import defaultdict
import heapq
def prim(vertexs, edges):
adjacent_vertex = defaultdict(list)
for v1, v2, length in edges:
adjacent_vertex[v1].append((length, v1, v2))
adjacent_vertex[v2].append((length, v2, v1))
"""
经过上述操作,将edges列表中各项归类成以某点为dictionary的key,其value则是其相邻的点以及边长。如下:
defaultdict(<type 'list'>, {'A': [(7, 'A', 'B'), (5, 'A', 'D')],
'C': [(8, 'C', 'B'), (5, 'C', 'E')],
'B': [(7, 'B', 'A'), (8, 'B', 'C'), (9, 'B', 'D'), (7, 'B', 'E')],
'E': [(7, 'E', 'B'), (5, 'E', 'C'), (15, 'E', 'D'), (8, 'E', 'F'), (9, 'E', 'G')],
'D': [(5, 'D', 'A'), (9, 'D', 'B'), (15, 'D', 'E'), (6, 'D', 'F')],
'G': [(9, 'G', 'E'), (11, 'G', 'F')],
'F': [(6, 'F', 'D'), (8, 'F', 'E'), (11, 'F', 'G')]})
"""
res = [] # 存储最小生成树结果
# vertexs是顶点列表,vertexs = list("ABCDEFG") == = > vertexs = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G']
visited = set(vertexs[0])
# 得到adjacent_vertexs_edges中顶点是'A'(nodes[0]='A')的相邻点list,即adjacent_vertexs['A']=[(7,'A','B'),(5,'A','D')]
adjacent_vertexs_edges = adjacent_vertex[vertexs[0]]
# 将usable_edges加入到堆中,并能够实现用heappop从其中动态取出最小值。关于heapq模块功能,参考python官方文档
heapq.heapify(adjacent_vertexs_edges)
while adjacent_vertexs_edges:
# 得到某个定点(做为adjacent_vertexs_edges的键)与相邻点距离(相邻点和边长/距离做为该键的值)最小值
w, v1, v2 = heapq.heappop(adjacent_vertexs_edges)
if v2 not in visited:
# 在used中有第一选定的点'A',上面得到了距离A点最近的点'D',举例是5。将'd'追加到used中
visited.add(v2)
# 将v1,v2,w,第一次循环就是('A','D',5) append into res
res.append((v1, v2, w))
# 再找与d相邻的点,如果没有在heap中,则应用heappush压入堆内,以加入排序行列
for next_vertex in adjacent_vertex[v2]:
if next_vertex[2] not in visited:
heapq.heappush(adjacent_vertexs_edges, next_vertex)
return res
# test
vertexs = list("ABCDEFG")
edges = [("A", "B", 7), ("A", "D", 5),
("B", "C", 8), ("B", "D", 9),
("B", "E", 7), ("C", "E", 5),
("D", "E", 15), ("D", "F", 6),
("E", "F", 8), ("E", "G", 9),
("F", "G", 11)]
print("edges:", edges)
print("prim:", prim(vertexs, edges))
Dijkstra[单源最短路径算法]
- Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的单源最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径
- 以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止
- 要求图中不存在负权边


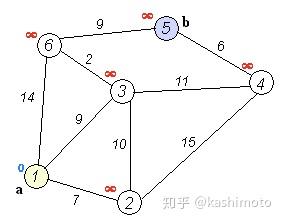
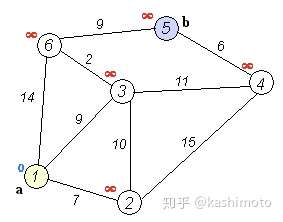
import sys
def dijkstra(graph):
n = len(graph)
dist = [sys.maxsize] * n
dist[0] = 0 # 自己和自己距离为0
visited = set()
def minDistance():
# 找到还没确定的里面距离最小的
min_ans, min_index = min((dis, i)
for i, dis in enumerate(dist) if i not in visited)
return min_index
for _ in range(n):
min_index = minDistance()
# 已经确定了
visited.add(min_index)
for v in range(n):
if v not in visited and graph[min_index][v] > 0:
# graph[min_index][v] > 0 表示存在这个路径
new_dist = dist[min_index] + graph[min_index][v]
if dist[v] > new_dist: # 表示值得被更新
dist[v] = new_dist
print(dist)
# Driver program
graph = [[0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0],
[0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6],
[8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0]]
dijkstra(graph)
Floyd[任意两点间的最短路径]
a.从任意一条单边路径开始。所有两点之间的距离是边的权,如果两点之间没有边相连,则权为无穷大。
b.对于每一对顶点 u 和 v,看看是否存在一个顶点 w 使得从 u 到 w 再到 v 比己知的路径更短。如果是更新它。
Inf = 65535 # 代表无穷大
arr = [[0, 10, Inf, Inf, Inf, 11, Inf, Inf, Inf], # 邻接矩阵
[10, 0, 18, Inf, Inf, Inf, 16, Inf, 12],
[Inf, 18, 0, 22, Inf, Inf, Inf, Inf, 8],
[Inf, Inf, 22, 0, 20, Inf, Inf, 16, 21],
[Inf, Inf, Inf, 20, 0, 26, Inf, 7, Inf],
[11, Inf, Inf, Inf, 26, 0, 17, Inf, Inf],
[Inf, 16, Inf, 24, Inf, 17, 0, 19, Inf],
[Inf, Inf, Inf, 16, 7, Inf, 19, 0, Inf],
[Inf, 12, 8, 21, Inf, Inf, Inf, Inf, 0]]
n = len(arr) # 邻接矩阵大小
path = [[-1]*n for _ in range(n)]
for k in range(n): # k在第一层
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if(arr[i][j] > arr[i][k]+arr[k][j]): # 两个顶点直接较小的间接路径替换较大的直接路径
arr[i][j] = arr[i][k]+arr[k][j]
path[i][j] = k # 记录新路径的前驱
for x in arr:
print(x)
print()
for x in path:
print(x)
字符串算法
KMP
class Solution(object):
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
:type haystack: str
:type needle: str
:rtype: int
"""
if not needle: return 0
# build next
next = [0]*len(needle)
l, r = 0, 1
while r < len(needle):
if needle[l] == needle[r]:
next[r] = l+1
l, r = l+1, r+1
elif l: l = next[l-1]
else: r += 1
# find idx
l, r = 0, 0
while r < len(haystack):
if needle[l] == haystack[r]:
if l == len(needle)-1:
return r-l
l, r = l+1, r+1
elif l: l = next[l-1]
else: r += 1
return -1
Rabin-Karp Hash
class RabinKarpHash:
def __init__(self, base, mod=int(1e9+7)):
self.base = base
self.mod = mod
def hash(self, arr):
h = 0
for val in arr:
h = ((h * self.base) + val) % self.mod
return h
def roll(self, origin_hash, drop_val, new_val, max_base):
h = origin_hash - (drop_val * max_base % self.mod)
h = ((h*self.base)+new_val+self.mod)%self.mod
return h
def get_max_base(self, length):
ret = 1
for i in range(length-1):
ret = (ret*self.base) % self.mod
return ret
Manacher’s Algorithm
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/manachers-algorithm-linear-time-longest-palindromic-substring-part-4/
def findLongestPalindromicString(text):
length = len(text)
if length == 0:
return
N = 2*length+1 # Position count
L = [0] * N
L[0] = 0
L[1] = 1
C = 1 # centerPosition
R = 2 # centerRightPosition
i = 0 # currentRightPosition
iMirror = 0 # currentLeftPosition
maxLPSLength = 0
maxLPSCenterPosition = 0
diff = -1
for i in range(2, N):
# get currentLeftPosition iMirror for currentRightPosition i
iMirror = 2*C-i
L[i] = 0 # 初始化范围
diff = R - i # 当前位置离上一个边界的距离
# If currentRightPosition i is within centerRightPosition R
if diff > 0: # 利用对称性获取L[i]的最小值
L[i] = min(L[iMirror], diff)
# 计算当前palindrome长度
while (True):
# 边界条件
con1 = (i + L[i]) < N and (i - L[i]) > 0
if (not con1):
break
# 奇数位置需要比较char
# 偶数位置直接加一
con2 = (i + L[i]) % 2 == 1
left_radius = int((i + L[i] + 1) / 2)
right_radius = int((i - L[i] - 1) / 2)
con31 = 0 <= left_radius and left_radius < length
con32 = 0 <= right_radius and right_radius < length
con3 = con31 and con32 and (text[left_radius] == text[right_radius])
if(con2 or con3):
L[i] += 1
else:
break
if L[i] > maxLPSLength: # Track maxLPSLength
maxLPSLength = L[i]
maxLPSCenterPosition = i
# 触及上一个边界的话选择center
if i + L[i] > R:
C = i
# 更新边界为当前的边界
R = i + L[i]
# Uncomment it to print LPS Length array
# printf("%d ", L[i]);
start = int((maxLPSCenterPosition - maxLPSLength) / 2)
end = int(start + maxLPSLength)
print(text[start:end])
# Driver program
text1 = "babcbabcbaccba"
findLongestPalindromicString(text1)
链表相关
优雅地遍历链表
while head:
head = head.next
standard linked list reversing
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head):
cur, prev = head, None
while cur:
cur.next, cur, prev = prev, cur.next, cur # standard reversing
return prev
merge sort list
class Solution(object):
def merge(self, h1, h2):
dummy = tail = ListNode(None)
while h1 and h2:
if h1.val < h2.val:
tail.next, tail, h1 = h1, h1, h1.next
else:
tail.next, tail, h2 = h2, h2, h2.next
tail.next = h1 or h2
return dummy.next
def sortList(self, head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head
pre, slow, fast = None, head, head
while fast and fast.next:
pre, slow, fast = slow, slow.next, fast.next.next
pre.next = None
return self.merge(self.sortList(head), self.sortList(slow))
二分
标准二分(bisect)
永远是lo = mid+1, hi = mid,返回lo,lo=0, hi=n
# 等价于 bisect
# 保证 选的数>k 严格大于
def bisect_right(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):
lo, hi = 0, n
while lo < hi:
mid = (lo+hi)//2
if x < a[mid]:
hi = mid # disgard equals part
else:
lo = mid+1
return lo
# bisect_left is more useful at hand, since it returns the exact index of the element being looked up if it is present in the list
# 保证 选的数>=k 大于等于
def bisect_left(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):
lo, hi = 0, n
while lo < hi:
mid = (lo+hi)//2
if a[mid] < x:
lo = mid+1 # disgard equals part
else:
hi = mid
return lo
>>> import bisect
>>> bisect.bisect_left([1,2,3], 2)
1
>>> bisect.bisect_right([1,2,3], 2)
2
范围都是[0-n]
import bisect
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], -1)) # 0
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], 0)) # 0
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], 1)) # 0
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], 2)) # 1
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], 3)) # 2
print(bisect.bisect_left([1, 2, 3], 4)) # 3
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], -1)) # 0
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], 0)) # 0
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], 1)) # 1
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], 2)) # 2
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], 3)) # 3
print(bisect.bisect([1, 2, 3], 4)) # 3
二分最优问题
都是 (lo+hi)//2, helper(mid) >= K, hi = mid-1, lo = mid+1
# 最大
# 找到最大的mid使得helper(mid)>=K
lo, hi = 1, sum(sweetness)
while lo <= hi:
# 找到最大的mid使得count>=K
mid = (lo+hi)//2
if helper(mid) >= K: # mid还可以再大一点
lo = mid+1
else:
hi = mid-1
return hi # 返回的是hi
# 最小
# 找到最小的mid使得helper(mid)>=K
lo, hi = 1, sum(sweetness)
while lo <= hi:
# 找到最大的mid使得count>=K
mid = (lo+hi)//2
if helper(mid) >= K: # mid还可以再大一点
hi = mid-1
else:
lo = mid+1
return lo # 返回的是lo
搜索算法
并查集 Union-Find Set (General)
class UF:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = list(range(n+1))
def find(self, i):
if self.parent[i] != i: # 用i来判断
self.parent[i] = self.find(self.parent[i]) # 路径压缩
return self.parent[i]
def union(self, x, y):
self.parent[self.find(x)] = self.find(y)
回溯法通用模板
def combine(self, n, k):
ans = []
def helper(cur, start):
if len(cur) == k:
ans.append(cur[:])
return
else:
for i in range(start+1, n+1):
cur.append(i)
helper(cur, i)
cur.pop()
helper([], 0)
return ans
A星算法核心公式
F = G + H
F - 方块的总移动代价 G - 开始点到当前方块的移动代价 H - 当前方块到结束点的预估移动代价[heuristic]
import heapq
def heuristic(a, b):
return (b[0] - a[0]) ** 2 + (b[1] - a[1]) ** 2
def astar(array, start, destination):
n, m = len(array), len(array[0])
dirs = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0),
(1, 1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (-1, -1)]
visited = set()
came_from = {}
gscore = {start: 0}
fscore = {start: heuristic(start, destination)}
queue = []
heapq.heappush(queue, (fscore[start], start))
while queue:
score, cur_pos = heapq.heappop(queue)
if cur_pos == destination:
data = []
while cur_pos in came_from:
data.append(cur_pos)
cur_pos = came_from[cur_pos]
return data
visited.add(cur_pos)
for i, j in dirs:
x, y = cur_pos[0] + i, cur_pos[1] + j
neibor = (x, y)
g = gscore[cur_pos]
h = heuristic(cur_pos, neibor)
f = g+h
if (not(0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < m) # 不能越界
or array[x][y] == 1 # 墙不能走
or(neibor in visited and f >= gscore.get(neibor, 0))): # 还不如从0直接过来
continue
if g < gscore.get(neibor, 0) or neibor not in [i[1]for i in queue]:
came_from[neibor] = cur_pos
gscore[neibor] = g
fscore[neibor] = g + \
heuristic(neibor, destination)
heapq.heappush(queue, (fscore[neibor], neibor))
return False
nmap = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
print(astar(nmap, (0, 0), (10, 13)))
def heuristic(a, b):
(x1, y1) = a
(x2, y2) = b
return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2)
def a_star_search(graph, start, goal):
frontier = PriorityQueue()
frontier.put(start, 0)
came_from = {}
cost_so_far = {}
came_from[start] = None
cost_so_far[start] = 0
while not frontier.empty():
current = frontier.get()
if current == goal:
break
for next in graph.neighbors(current):
new_cost = cost_so_far[current] + graph.cost(current, next)
if next not in cost_so_far or new_cost < cost_so_far[next]:
cost_so_far[next] = new_cost
priority = new_cost + heuristic(goal, next)
frontier.put(next, priority)
came_from[next] = current
return came_from, cost_so_far
数学方法
素数筛法
# 1不是素数,最小的质数是2
# Prime table
maxInteger = 1000000
prime = [True]*maxInteger
prime[0] = False
prime[1] = False
for i in range(2, (int)(math.sqrt(maxInteger)+1)):
if prime[i]:
for j in range(i*i, maxInteger, i):
prime[j] = False
求因数
# Given a list A, return all prime factors of elements in A
def getAllFactors(A):
factors = []
for x in A:
facs = []
# 筛法优化
k, d = 0, primes[k]
while d * :
if x % d == 0:
while x % d == 0:
x //= d
facs.append(d)
k += 1
d = primes[k]
# 特判,x>1说明有残余的质数,not facs说明x本身是质数
if x > 1 or not facs:
facs.append(x)
factors.append(facs)
黄金比例求斐波那契
class Solution:
def fib(self, N):
golden_ratio = (1 + 5 ** 0.5) / 2
return int((golden_ratio ** N + 1) / 5 ** 0.5)
$$ \phi=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2} \approx 1.61803 $$
快速幂
def fastExpMod(a, b):
res = 1
while b:
if (b & 1):
# ei = 1, then mul
res *= a
b >>= 1
# b, b^2, b^4, b^8, ... , b^(2^n)
a *= a
return res
牛顿法
class Solution:
def mySqrt(self, x):
r = x + 1 # avoid dividing 0
while r*r > x:
r = int((r+x/r)/2) # newton's method
return r
GCD
def gcd(a, b):
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
求多个数的GCD
def arr_gcd(self, A):
gcd = A[0]
for a in A:
while a:
gcd, a = a, gcd % a
return gcd
graycode
def grayCode(n):
res = [0]
i = 0
while i < n: # 从2的0次方开始,
next_base = 1 << i
res_inv = [x + next_base for x in reversed(res)]
res.extend(res_inv)
i += 1
return res
# 长度为4的所有graycode
# 用于遍历所有情况
# 0000
# 0001
# 0011
# 0010
# 0110
# 0111
# 0101
# 0100
# 1100
# 1101
# 1111
# 1110
# 1010
# 1011
# 1001
# 1000
专用方法
单调栈
def foo(nums):
st = []
res = [0]*len(nums)
for i, x in enumerate(nums):
while st and nums[st[-1]] < x:
idx = st.pop()
res[idx] = i-idx
st.append(i)
return res
slide window
一个for 一个 while 不容易出错
class Window:
def __init__(self):
self.count = collections.Counter()
self.reserve = 0
def add(self, x):
if self.count[x] == 0: # 从效果上来判断
self.reserve += 1
self.count[x] += 1
def remove(self, x):
self.count[x] -= 1
if self.count[x] == 0: #
self.reserve -= 1
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(self, A, K):
if not A or not len(A) or not K:
return 0
win = Window()
ans = l = 0
# 一个for 一个 while 不容易出错
for r, x in enumerate(A):
win.add(x)
while win.reserve > K:
win.remove(A[l])
l += 1
ans = max(r-l+1, ans)
return ans
二维数组前缀和
n, m = len(grid), len(grid[0])
pre_sum = [[0]*(m+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
pre_sum[i][j] = pre_sum[i][j-1] + \
pre_sum[i-1][j] - pre_sum[i-1][j-1] + grid[i][j]
def get_sum(x0, y0, x1, y1):
return pre_sum[x1][y1] - pre_sum[x0-1][y1] - pre_sum[x1][y0-1] + pre_sum[x0-1][y0-1]
def helper(size):
cur_max_sum = max(get_sum(x, y, x+size-1, y+size-1)
for x in range(n-size+1) for y in range(m-size+1))
return cur_max_sum
RMQ/ST[Sparse Table]算法
import math
class ST:
def __init__(self, arr):
self.arr = arr
self.n = n = len(arr)
self.m = m = int(math.log(n, 2))
self.maxsum = maxsum = [[0]*(m+1) for _ in range(n)]
self.minsum = minsum = [[0]*(m+1) for _ in range(n)]
for i, x in enumerate(arr):
maxsum[i][0] = minsum[i][0] = x
for j in range(m):
for i in range(n):
k = i + (1 << j)
if(k < n):
maxsum[i][j+1] = max(
maxsum[i][j], maxsum[k][j])
minsum[i][j+1] = min(
minsum[i][j], minsum[k][j])
def get_max(self, a, b):
k = int(math.log(b-a+1, 2))
# 一头一尾
return max(self.maxsum[a][k], self.maxsum[b-(1 << k)+1][k])
def get_min(self, a, b):
k = int(math.log(b-a+1, 2))
return min(self.minsum[a][k], self.minsum[b-(1 << k)+1][k])
arr = [3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 0, 3, 4, 5]
st = ST(arr)
print(st.get_max(0, 9)) # 9
print(st.get_max(6, 9)) # 5
print(st.get_min(0, 9)) # 0
print(st.get_min(0, 4)) # 3
LZ77
def compress(message):
win_size = 10 # 窗口长度
pointer = 0 # 指针,初始指向第一个位置
compressed_message = []
while pointer < len(message):
matched_length = 0 # 匹配到的长度
# 窗口的corner case
window = message[max(pointer - win_size, 0):pointer]
# 能找到的最大长度
while window.find(message[pointer:pointer + matched_length + 1]) != -1:
matched_length += 1
e = pointer + matched_length
# window.find(message[start:end]) 相对窗口的offset
# max(start - win_size, 0) 整个窗口的offset
# first:在整个字符串中的offset
first_appear = window.find(message[pointer:e]) + \
max(pointer - win_size, 0)
item = (pointer - first_appear, matched_length, message[e])
compressed_message.append(item)
pointer += matched_length + 1
return compressed_message
print(compress("abcdbbccaaabaeaaabaee"))
优雅地先序遍历
def preorder(self, root):
if (not root):
return ["null"]
return [str(root.val)]+self.preorder(root.left)+self.preorder(root.right)
def serialize(self, root):
return ",".join(self.preorder(root))