
baniol
5/30/2016 - 4:08 PM
React/Redux async api requests
React/Redux async api requests
React Redux Walkthrough, part 3
Asynchronous API requests
So far, our application gets data from a hardcoded collection passed as a default state to the employees reducer function. However, for most of the web applications data should be loaded asyncronously from a remote server. The goal of this part is to provide this functionality with proper unit tests.
The application source code
switch to the 03-asyn-api branch and run npm install.
Api server
For the purpose of moving the data out of our React/Redux application I've provided a simple API server based on Express framework (api-server folder). Executing npm start will spin up two node processes - one on port 3000 serving static assets of our application, another one on port 3001 providing JSON data from the API server. Pointing your browser to http://localhost:3001/employees you should see the employees collection.
As you can see in the api-server/routes/index.js, the reseponse is delayed by 1.5 second to simulate server/network latency, so we can see the preloading info.
Ok. So the first question should be: where do we trigger the http request? The answer being: as soon as our component that needs this data is loaded/mounted. React provides a life-cycle method that will serve the purpose: componentDidMount.
Actions
To make a web request we are going to use the isomorphic-fetch library (you can use others, like axios or superagent).
If we simply adjusted the action creator function to return a http promise instead of a plain object we would see an error: Actions must be plain objects. Use custom middleware for async actions. We will duly follow the advice and plug in the thunk library, that "can be used to delay the dispatch of an action, or to dispatch only if a certain condition is met." (check the src/index.js file for details).
If you want to know more about the motivation and internals of the library read this post on stack overflow
Now we are ready to make the API request and render the employee list. Let's take a look at the diagram:
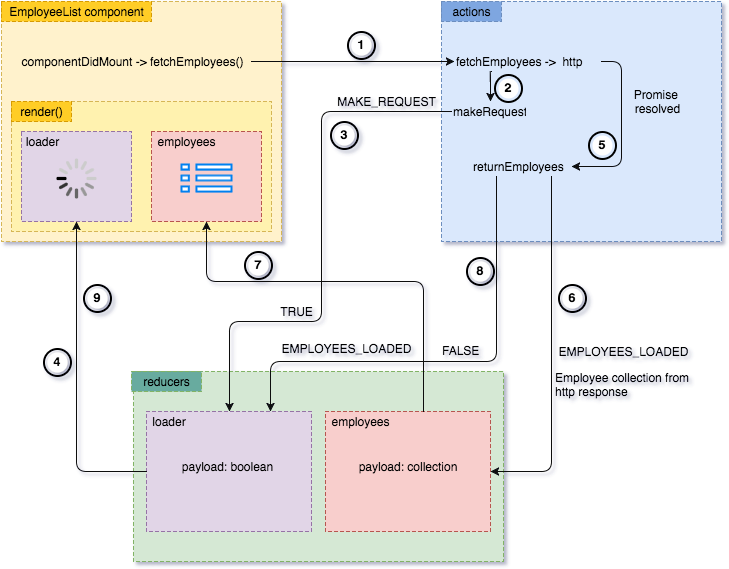
- When the
EmployeeListcomponent is loaded, thecomponentDidMountcalls thefetchEmployeesfunction, passed to the component viamapDispatchToPropsfunction. This dispatches thefetchEmployeesaction creator. makeRequestaction is dispatched.- The action creator returns
truechanging the loader state via theloaderreducer - Loader is being shown as a result of a loader state change.
- Back to the
fetchEmployeesaction creator. It returns a promise that when resolved dispatches thereturnEmployeesaction creator. - The action returns employee collection as a payload which alters the employee collection state.
- The employee list is rendered in the
EmployeeListcomponent. - The
returnEmployeesaction creator returns the loader property set tofalseas a payload. - Loader is being hidden in the
EmployeeListcomponent.
Unit testing async requests
To provide unit tests for our new async mechanism we have to add another two modules to our dev dependencies: redux-mock-store and nock.
Nock's task is to intercept the http requests and set appropriate return value. Using it, we are in control of the result of a mocked request. To use the dispatch method on the global store object we have to mock it first with redux-mock-store - initially, we set the employees state to an empty collection and to check it for the http result after dispatching the action creator.
Handling http errors
The last thing to do for our async requests is to provide a proper error handling for the API server response. We haven't done it yet for the sake of data flow clarity. To see the code changes checkout to the branch 03a-async-errors. To simulate an error, change the api url in the actions index.js - you should have the error displayed instead of the employee list.
To provide error handling, the following changes have been made:
- action creator
requestErroradded - EmployeeList modifications to display an error if the
errorstate is notnull - error reducer added
- a switch case 'REQUEST_ERROR' added to loader reducer
- unit tests for displaying errors in
EmployeeList component added
Debug middleware
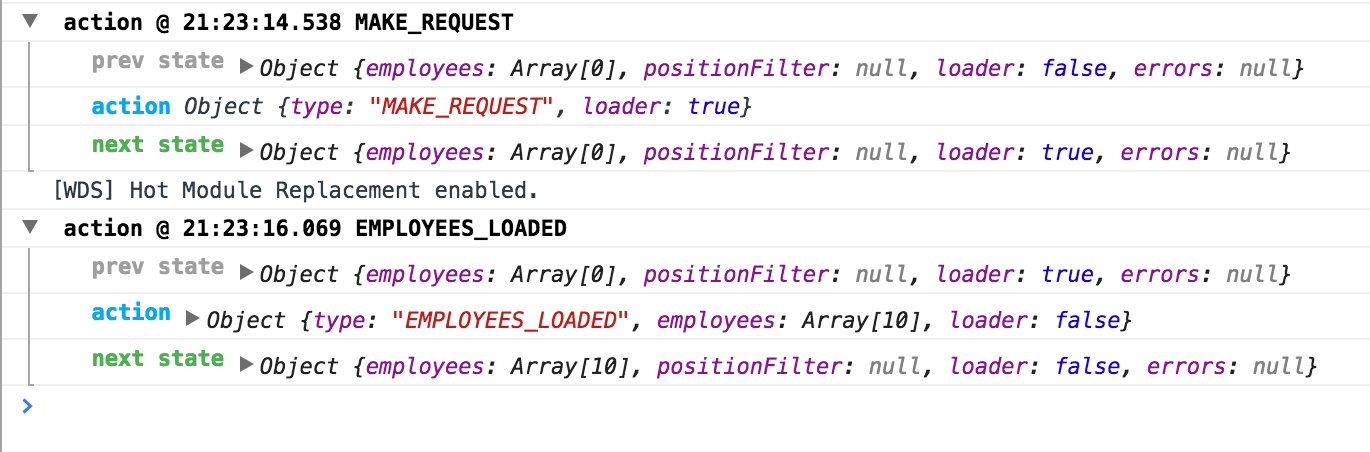
In addition to thunk we'll make use of redux-logger middleware that can help with debugging the application. Now, every dispatched action will be logged in the browser's console:
Thanks for reading the post and if it got you attention, I invite you to check the next part where I'll be writing about another important feature of single page applications - routing.